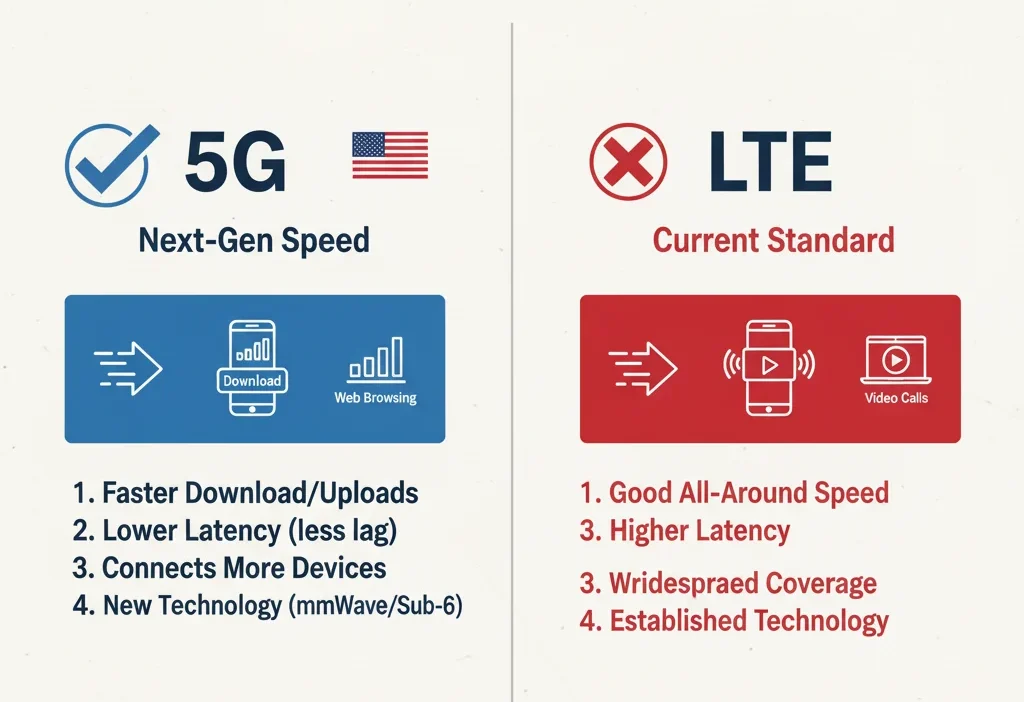
5G is the newer, faster, and more advanced network, while LTE is an older 4G network that is slower but still very reliable.
If you want super-fast internet, low delay, and better performance, choose 5G. If your area doesn’t support 5G yet, LTE works perfectly for everyday use.
Have you ever looked at your phone and wondered, “Should I use 5G or LTE?”
Many people get confused between these two network terms because both appear on smartphones, SIM packages, and internet settings. Even though they look similar, 5G and LTE are very different, just like comparing a brand-new sports car to a regular family car.
In this simple guide, you will learn:
- What 5G means
- What LTE means
- The difference between 5G and LTE
- When to use each one
- Common mistakes people make
- Easy examples anyone can understand
Everything is explained in clear, simple language so even a class 4 student can understand perfectly. Let’s begin!
What Does Each Term Mean?
What Is 5G?
5G means “Fifth Generation” mobile network.
It is the newest and fastest network available today.
Key Points About 5G
- Very fast internet speed
- Very low delay (pages and apps load instantly)
- Supports smart devices, gaming, and large downloads
- Best for modern smartphones
3 Easy Examples
- You download a movie in seconds using 5G.
- A video call feels smooth and never freezes on 5G.
- Online gaming works without lag because 5G responds very fast.
What Is LTE?
LTE stands for “Long-Term Evolution.”
It is a type of 4G network that is fast but not as advanced as 5G.
Key Points About LTE
- Good internet speed
- Works in most areas
- Best for normal daily use
- More stable in rural or weak-signal areas
3 Easy Examples
- Browsing Facebook or Instagram works smoothly on LTE.
- You can watch YouTube at HD quality on LTE.
- If 5G is not available, your phone will shift to LTE automatically.
The Key Difference Between 5G and LTE
Here is a simple comparison table to clearly show the difference between 5G and LTE:
| Feature | 5G | LTE (4G) |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Very fast (up to 10x faster than LTE) | Fast, but slower than 5G |
| Delay (Latency) | Very low | Moderate |
| Best Use | Gaming, HD video calls, fast downloads | Everyday browsing, apps, social media |
| Coverage | Still expanding | Available almost everywhere |
| Technology | Latest generation | Older generation |
Quick Tip to Remember
5G = Faster.
LTE = Reliable.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Mistake 1: Thinking LTE is 5G
Incorrect: “LTE means 5G.”
Correct: LTE is 4G, not 5G.
Why it happens:
The names look modern and similar.
How to fix:
Remember: If it doesn’t say 5G, it’s not 5G.
Mistake 2: Believing 5G Works Everywhere
Incorrect: “My phone supports 5G, so it will work everywhere.”
Correct: 5G only works where towers are installed.
Fix:
If 5G is weak in your area, switch to LTE for stability.
Mistake 3: Expecting 5G to Always Be Faster
Incorrect: “5G must always be faster than LTE.”
Correct: If 5G signal is weak, LTE may perform better.
Fix:
Choose the stronger signal instead of just the newer one.
When to Use 5G
Use 5G when you want the fastest and smoothest internet experience.
Best Situations for 5G
- Downloading large apps or games
- Watching 4K or HD movies
- Playing online games
- Doing video calls for work or school
- Using advanced apps like AR or VR
Example Sentences
- “I switched to 5G to download my game quickly.”
- “The video call looks clear on 5G.”
- “I use 5G when I need fast internet for work.”
When to Use LTE
Use LTE when 5G is weak, unavailable, or unnecessary.
Best Situations for LTE
- Normal browsing
- Social media
- Maps and navigation
- Sending messages
- When your battery is low (LTE uses less battery)
Example Sentences
- “My area has weak signal, so I use LTE.”
- “LTE is enough for scrolling Instagram.”
- “When my phone battery is low, I switch to LTE.”
Memory Hack
Think of LTE as the “safe mode” of your phone’s internet.
It always works and does not fail easily.
Quick Recap: 5G vs LTE
- 5G is faster, newer, and better for heavy tasks.
- LTE is stable, widely available, and perfect for daily use.
- Use 5G for fast downloads, gaming, and HD calls.
- Use LTE when 5G is weak or unnecessary.
- Both networks help your phone connect to the internet, but 5G is the next level.
Advanced Tips (Optional)
1. History of the Terms
- LTE was introduced around 2009 as an upgrade to 3G.
- 5G started rolling out around 2019 as a next-generation network.
2. Formal Usage
In technical writing, always write:
- “5G network”
- “LTE connection”
3. Online Writing Mistakes
Using “LTE” and “5G” wrongly in reviews or posts can confuse readers.
Example:
- Wrong: “This phone has LTE 5G.”
- Correct: “This phone supports both 5G and LTE.”
Mini Quiz (Test Yourself!)
Fill in the blanks:
- ______ is faster and newer than LTE.
- If 5G is weak, switch to ______.
- For online gaming, ______ is better.
- LTE is a type of ______ network.
- ______ works almost everywhere and uses less battery.
Conclusion
Now you clearly understand the meaning of 5G and LTE, how they differ, and when to use each one.
Choosing the right network can make your phone faster, smoother, and more reliable. Whether you want top performance with 5G or everyday stability with LTE, you now know exactly which one fits your needs.
Keep practicing, keep learning, and soon these tech terms will feel easy and familiar.
You’re improving your understanding every day — and that’s amazing!
FAQs
1. Which is better: 5G or LTE?
5G is better for speed and performance, while LTE is better for coverage and stability.
2. Does 5G drain more battery?
Yes, 5G can use more battery, especially in weak-signal areas.
3. Why does my phone switch between 5G and LTE?
Your phone chooses the signal that is stronger and more stable at the moment.
4. Can LTE be faster than 5G sometimes?
Yes. If 5G is weak, LTE may work faster and smoother.
5. Is 5G available everywhere?
Not yet. Coverage is still growing, so some areas may rely more on LTE

Francis Sufford crafts thoughtful, insightful explanations on language, meaning, and usage, blending clarity with storytelling to guide readers effectively.