Many learners mix up math symbols like the equal or less than sign (≤) with other comparison symbols such as less than (<) or equal to (=). It may look small, but using it wrongly can completely change the meaning of a sentence or equation!
In this simple 2025 guide, we’ll clearly explain what the equal or less than sign means, how it’s different from similar symbols, and where to use it correctly in math and English expressions. You’ll also learn simple grammar-style explanations, real examples, and easy tricks to remember it forever.
Whether you’re a student, teacher, or just brushing up on basics, this guide will make comparison signs easy to understand and fun to use. By the end, you’ll know exactly when to write ≤, what it means, and how to explain it like a pro!
What Does the Equal or Less Than Sign (≤) Mean?
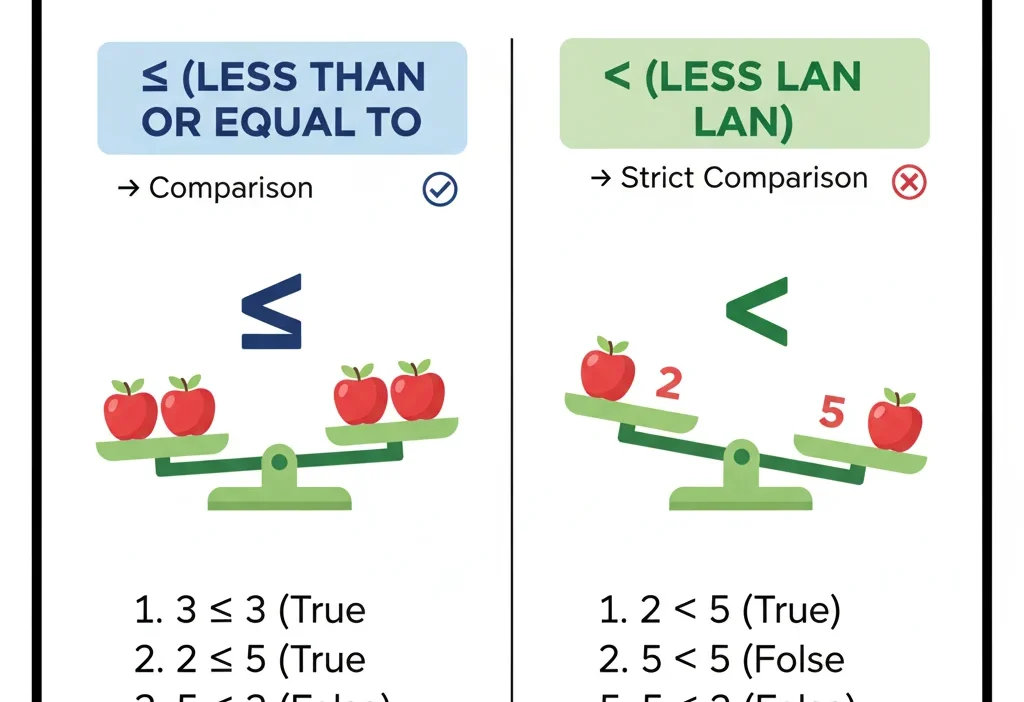
The equal or less than sign (≤) means that one number or quantity is either smaller than or equal to another number. It combines two ideas in one symbol — less than (<) and equal to (=).
In words, it reads as:
👉 “is less than or equal to.”
For example:
✅ 5 ≤ 8 → means 5 is less than 8.
✅ 8 ≤ 8 → means 8 is equal to 8.
So, the ≤ sign works for both conditions — being smaller or being equal.
Part of Speech (In Grammar Context):
While it’s not a “word,” in English grammar-like explanations, you can think of ≤ as a comparison operator — it shows a relationship between two values or ideas.
Tip to Remember:
Draw a line under the “<” sign. That line means “equals too!” — so ≤ = “less than or equal to.”
Difference Between “Equal or Less Than” and Other Comparison Signs
It’s easy to confuse ≤ with <, =, or ≥, but each has its own meaning.
Here’s a clear comparison chart to help you remember:
| Symbol | Meaning | Example | Reads As |
|---|---|---|---|
< | Less than | 5 < 7 | 5 is less than 7 |
≤ | Less than or equal to | 5 ≤ 7, 7 ≤ 7 | 5 is less than or equal to 7 |
> | Greater than | 9 > 4 | 9 is greater than 4 |
≥ | Greater than or equal to | 6 ≥ 6 | 6 is greater than or equal to 6 |
= | Equal to | 10 = 10 | 10 is equal to 10 |
Quick Tip 🧠:
- If it has a line underneath → it includes equality.
- If there’s no line → it’s a strict comparison (only less or greater).
How to Use the Equal or Less Than Sign (≤) Correctly
You’ll use ≤ when you want to say that one number is smaller than or could be the same as another.
✅ Examples:
- The number of apples ≤ 10 (You can have up to 10 apples.)
- x ≤ 5 means x can be any number smaller than or equal to 5.
- Your score must be ≤ 100. (It can’t be more than 100.)
- The temperature should be ≤ 25°C. (No higher than 25°C.)
- I will arrive at or before 7 p.m. → Time ≤ 7 p.m.
Grammar Tip:
Think of “≤” as saying “no more than” or “at most.”
For example:
- “You can take at most 3 pencils.” → means pencils ≤ 3.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Even though ≤ looks simple, students often mix it up with <, =, or even ≥. Here are some common examples and how to fix them:
| ❌ Incorrect | ✅ Correct | Why? |
|---|---|---|
| 5 < 5 | 5 ≤ 5 | Because 5 is not less than 5, but it is equal to 5. |
| The value ≤ 10 → written as < 10 | Keep ≤ | You include the case when value = 10. |
| x ≥ 3 when you mean “3 or less” | x ≤ 3 | Wrong direction of inequality! |
Memory Hack 🔍:
👉 The arrow in ≤ always points to the smaller number.
Example: 3 ≤ 8 → The open side faces the larger number (8).
When to Use the Equal or Less Than Sign (≤)
You’ll see ≤ in math, logic, and even simple writing to describe limits or boundaries.
1. In Math Problems:
Used in inequalities to define limits.
Example: “x ≤ 10” means x can be 10 or any smaller number.
2. In Real-Life Contexts:
- Age Limits: Children aged ≤ 12 get a discount.
- Speed Limits: Cars must go ≤ 60 km/h.
- Prices: You can buy items priced ≤ $50.
3. In English Sentences (Grammar Context):
Used as part of descriptive comparisons.
Example: “The number of guests should be equal to or less than fifty.”
4. In Statistics or Data:
- Probability values: P(x ≤ 0.5)
- Cumulative frequency charts
5. In Technology or Programming:
In most coding languages (Python, Excel, etc.), you write <= instead of ≤.
Example:
if (score <= 100):
print("Valid score")
When NOT to Use the Equal or Less Than Sign
Avoid using ≤ when:
- You mean “greater than” or “more than.”
- You are describing equality only (then just use =).
- You’re writing informal text—use words like “no more than” or “at most” in essays.
Example:
❌ The cost ≤ $20 → (not ideal in normal writing)
✅ The cost is less than or equal to $20 → (better in sentences)
Equal or Less Than vs Less Than — What’s the Difference?
This is one of the most confusing points for students! Let’s make it simple:
| Feature | Less Than (<) | Equal or Less Than (≤) |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Smaller only | Smaller or exactly equal |
| Example | 4 < 5 | 4 ≤ 5 or 5 ≤ 5 |
| Includes Equality? | ❌ No | ✅ Yes |
| Used When | Comparing only smaller values | Allowing equality too |
Quick Example:
- “You must score less than 60 to fail.” → < 60 (If you score exactly 60, you pass.)
- “You must score 60 or less to fail.” → ≤ 60 (Even if you score 60, you fail.)
Mini Grammar Connection: “Then or Than” Confusion
You might wonder — what does this have to do with grammar?
Actually, the equal or less than concept works like then vs than in grammar — both show comparison and sequence ideas!
- “Then” = time or order → like moving from one number to another.
- “Than” = comparison → just like <, >, ≤, or ≥.
Example:
- “5 is smaller than 6.” → That’s where “than” comes from!
So when you say “less than”, you’re actually using “than” for comparison — just like a math sign!
Quick Recap: Equal or Less Than (≤) Summary
✅ Meaning: One value is smaller than or the same as another.
✅ Symbol: ≤
✅ Reads As: “is less than or equal to.”
✅ Examples:
- 3 ≤ 4 (True)
- 8 ≤ 8 (True)
- 9 ≤ 2 (False)
✅ Real-Life Use:
- Age ≤ 18 → child ticket
- Weight ≤ 50kg → safe limit
- Time ≤ 10 seconds → success
✅ Memory Trick:
If the symbol has a line underneath, it includes equality too!
Advanced Tips for Learners (2025 Update)
- History: The ≤ symbol was first introduced by English mathematician Thomas Harriot in the 1600s.
- Typing Tip: You can type ≤ using these shortcuts:
- Windows:
Alt + 243 - Mac:
Option + <
- Windows:
- In Formal Writing: It’s fine to write out “less than or equal to” instead of using the symbol.
- In Programming: Always use <= because computers don’t understand the symbol ≤ directly.
- Common Mistake: Don’t reverse it accidentally! ≤ means “less,” ≥ means “greater.”
Mini Quiz — Test Yourself!
Fill in the blanks with the correct symbol: <, ≤, >, or ≥
- 6 ___ 6
- 3 ___ 7
- 10 ___ 9
- Price must be ___ $100.
- x ___ 5 means x is not more than 5.
Answers:
- ≤
- <
- ≤
- ≤
FAQs (Featured Snippet Ready)
Q1: What does the equal or less than sign mean?
It means one value is smaller than or exactly equal to another. Example: 5 ≤ 8.
Q2: How do you write equal or less than in words?
Say “less than or equal to.” Example: “The total must be less than or equal to 10.”
Q3: What’s the difference between < and ≤?
“<” means smaller only; “≤” includes being equal too.
Q4: How can I type ≤ on my keyboard?
Windows: Hold Alt + 243. Mac: Press Option + <.
Q5: What’s a real-life example of ≤?
“Children aged ≤ 12 ride free” — means children up to 12 years old.
Conclusion
Now you clearly know what equal or less than (≤) means and how to use it correctly.
Remember: ≤ = less or equal. It’s like saying “no more than” or “up to.”
Whether you’re solving math problems, writing rules, or explaining comparisons, this small sign makes a big difference.
Keep practicing with simple examples and you’ll soon recognize it instantly.
Learning these tiny details helps you not only in math but also in logical thinking and grammar-style comparisons. Stay curious — every symbol tells a story!

Gwendoline Riley delivers clear, compelling insights into language and usage, helping readers understand meanings, nuances, and differences with confidence.