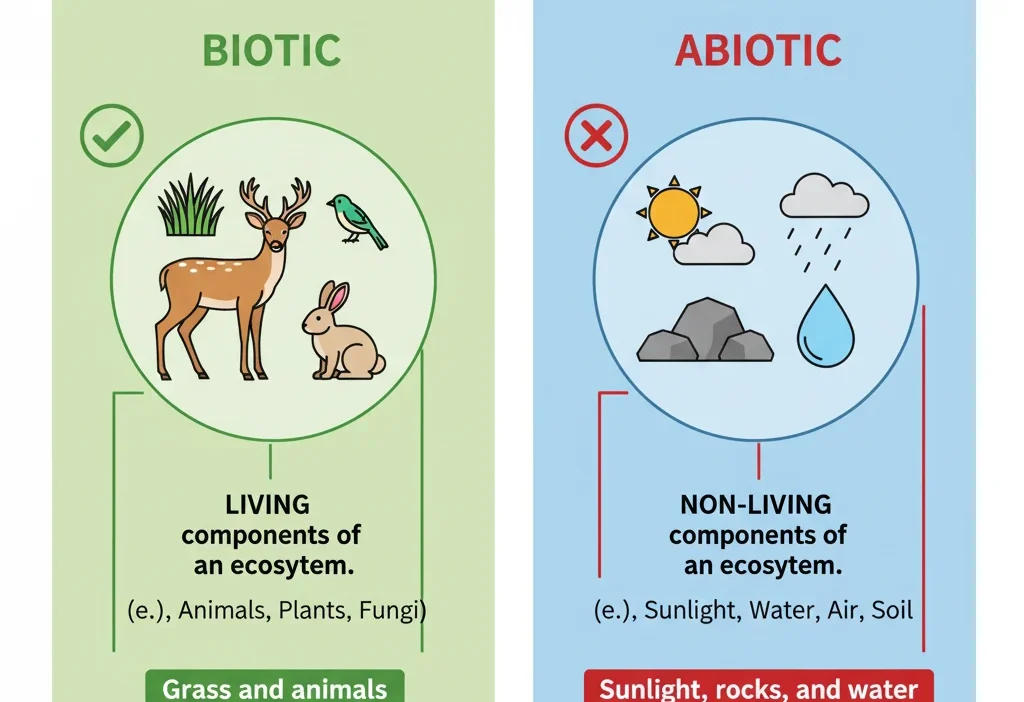
Grass is biotic because it is a living organism that grows, reproduces, and interacts with its environment. Abiotic factors, on the other hand, are non-living elements like sunlight, soil, and water.
Have you ever wondered whether grass is biotic or abiotic? It might sound tricky at first, but once you understand the meaning of these words, it becomes simple. Many students and beginners confuse biotic and abiotic because both words are commonly used in science and environmental studies.
In this guide, you will learn:
- The exact meanings of biotic and abiotic
- How to easily remember which is which
- Common mistakes and how to avoid them
- Real-life examples that make the difference crystal clear
By the end of this article, even beginners will confidently answer: “Grass is biotic or abiotic?” without hesitation.
What Does Each Word Mean? 🌍
1. Biotic
Definition: Biotic refers to living things in an ecosystem. These are organisms that grow, reproduce, and interact with other living things.
Part of Speech: Adjective
Examples:
- Grass is biotic because it grows and reproduces.
- Trees, flowers, and animals are all biotic components of nature.
- Bacteria in the soil are biotic even though we cannot see them.
Story Tip: Imagine a garden — every plant, insect, and bird you see is biotic. They are alive and active.
2. Abiotic
Definition: Abiotic refers to non-living things in an ecosystem. These cannot grow, reproduce, or carry out life processes.
Part of Speech: Adjective
Examples:
- Sunlight is abiotic because it is not alive.
- Water, rocks, and soil are abiotic factors that support life.
- Temperature and climate are abiotic elements affecting living organisms.
Story Tip: Think of the sun and the rocks in a garden — they are important but not alive.
The Key Difference Between Grass Biotic or Abiotic 🌱💧
| Feature | Biotic (Living) | Abiotic (Non-Living) |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Living organisms | Non-living components |
| Can grow/reproduce? | Yes | No |
| Examples | Grass, animals, trees, bacteria | Water, soil, sunlight, rocks |
| Usage Tip | Use for living things | Use for non-living things |
Quick Tip: If it breathes, grows, or moves, it’s biotic. If it doesn’t, it’s abiotic.
Soil Homogeneous or Heterogeneous: The Hidden Truth Revealed
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them ❌✅
Mistake 1: Saying, “Grass is abiotic.”
Correction: “Grass is biotic.”
Why: Grass is alive; abiotic only applies to non-living things like soil or sunlight.
Mistake 2: Confusing water as biotic.
Correction: Water is abiotic.
Why: Water supports life but is not alive itself.
Mistake 3: Calling bacteria abiotic.
Correction: Bacteria is biotic.
Why: Even microscopic organisms are living.
Tip to avoid mistakes: Always ask, “Is it alive?”
When to Use Biotic 🌿
Use biotic for all living components in an ecosystem.
Examples in Real Life:
- Grass is biotic because it grows in fields.
- Birds in the park are biotic.
- Flowers in your garden are biotic.
- Fish in the pond are biotic.
- Bacteria in soil are biotic.
Memory Hack: Think “Biotic = Breathes or grows.”
When to Use Abiotic 💧
Use abiotic for non-living environmental factors.
Examples in Real Life:
- Sunlight is abiotic because it provides energy but does not grow.
- Rocks are abiotic because they cannot move or reproduce.
- Soil is abiotic even though it supports plants.
- Rain is abiotic because it falls but is not alive.
Quick Recap: Grass Biotic or Abiotic 🌱💡
- Biotic: Living things, can grow and reproduce → grass, trees, animals
- Abiotic: Non-living things, cannot grow → water, soil, sunlight
- Easy Rule: “Alive = Biotic, Not Alive = Abiotic”
Advanced Tips (Optional) ✨
- The terms biotic and abiotic come from Greek: bios = life, a- = without.
- In essays or science exams, correctly identifying biotic vs abiotic can earn points.
- Misusing these terms in online posts or assignments may confuse readers.
- Remember: Every ecosystem is a mix of biotic and abiotic factors working together.
Mini Quiz: Test Your Knowledge ✅
Fill in the blanks:
- Grass is _______ because it grows and reproduces.
- Sunlight is _______ because it is not alive.
- Fish in a pond are _______.
- Rocks in a mountain are _______.
- Bacteria in soil are _______.
- Rain is _______ and essential for plants.
- Trees are _______ because they can produce seeds.
(Answers: 1. Biotic, 2. Abiotic, 3. Biotic, 4. Abiotic, 5. Biotic, 6. Abiotic, 7. Biotic)
Conclusion
Now you know the difference between biotic and abiotic! Grass, being alive, is always biotic. Abiotic factors like sunlight, water, and soil support life but are not living. By practicing the examples and memory hacks in this guide, you can easily identify living and non-living things in any ecosystem.
Keep practicing, and soon answering questions like “Grass biotic or abiotic?” will be second nature. Remember, learning English and science is fun when you see it in real life every day!
FAQs
Q1: Is grass considered abiotic in any situation?
A1: No. Grass is always biotic because it is a living organism.
Q2: Can water ever be biotic?
A2: No. Water is abiotic, but it supports biotic life.
Q3: Are microscopic organisms like bacteria biotic?
A3: Yes. Bacteria are living organisms, so they are biotic.
Q4: What is the easiest way to remember biotic vs abiotic?
A4: Ask: “Is it alive?” If yes → biotic. If no → abiotic.
Q5: Why is knowing biotic and abiotic important?
A5: It helps understand ecosystems, environmental science, and biology.

Gwendoline Riley delivers clear, compelling insights into language and usage, helping readers understand meanings, nuances, and differences with confidence.