Energy can be potential OR kinetic.
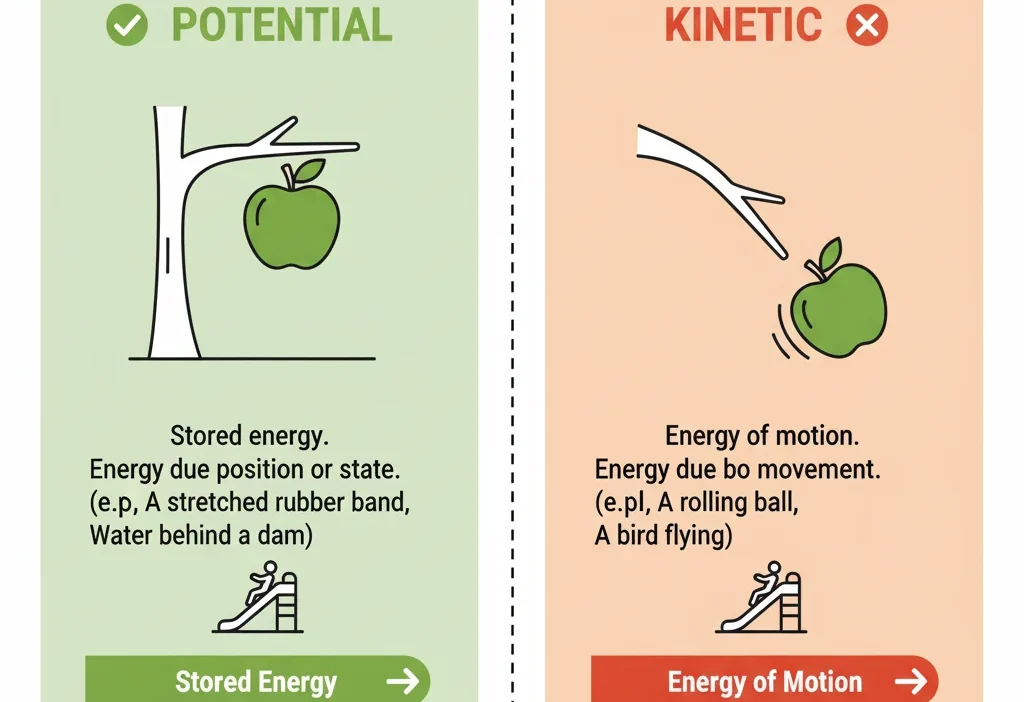
- Potential energy = stored energy.
- Kinetic energy = moving energy.
If something is not moving but can move → Potential
If something is moving → Kinetic.
Have you ever wondered “Is energy potential or kinetic?” or felt confused when teachers talk about different “types of energy”? Don’t worry — you’re not alone. Many students mix up these two terms because they sound scientific and similar. But the good news is: the difference between potential and kinetic energy is actually very simple, and anyone — even a 4th-grader — can easily understand it with the right examples.
In this friendly, step-by-step guide, you’ll learn exactly what potential energy means, what kinetic energy means, how they are different, when to use each one correctly, and how to remember them forever using super simple tricks.
By the end, you’ll understand potential vs kinetic energy so clearly that you can explain it to your friends, siblings, or even your teacher!
What Does Each Word Mean?
What Is Potential Energy? (Simple Definition)
Potential energy is stored energy.
It is the energy something has because of its position, height, or shape.
Part of Speech: Noun (a type of energy)
Easy Examples of Potential Energy
- A book sitting on a shelf (it can fall — energy is stored).
- A stretched rubber band (it can snap back).
- Water behind a dam (waiting to move).
Imagine you’re holding a ball high in the air. It’s not moving, but it has stored power because gravity can pull it down. That stored power is potential energy.
What Is Kinetic Energy? (Simple Definition)
Kinetic energy is moving energy.
Any object that is moving has kinetic energy.
Part of Speech: Noun (a type of energy)
Easy Examples of Kinetic Energy
- A running boy
- A car driving on the road
- A rolling ball
If that ball you were holding starts falling — now it has kinetic energy because it’s moving!
The Key Difference Between Potential Energy and Kinetic Energy
The easiest way to understand the difference:
Potential energy = Not moving but can move
Kinetic energy = Moving right now
Comparison Table: Potential vs Kinetic Energy
| Feature | Potential Energy | Kinetic Energy |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Stored energy | Energy of movement |
| Object State | Not moving | Moving |
| Example | Book on a shelf | Book falling |
| Depends On | Height, position, shape | Speed and mass |
| Simple Clue | “Has the power” | “Is doing it” |
Quick Tip to Remember
P = Parking → Potential energy is like a parked car.
K = Kicking → Kinetic energy is like kicking a ball (movement).
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
❌ Mistake 1: “Anything high is kinetic energy.”
✔ Correct: Height gives potential, not kinetic.
A bird sitting on a tree still has potential energy unless it starts flying.
❌ Mistake 2: “Fast things have potential energy.”
✔ Correct: Fast things have kinetic energy, because they are moving.
❌ Mistake 3: “Something can only have one type of energy.”
✔ Correct: Some objects can switch from potential → kinetic easily.
Example: A roller coaster at the top (potential) → going down (kinetic)
When to Use Potential Energy
Use potential energy when:
- The object is not moving
- The object has height, stored power, or stretch
- The object could move because of its condition
Examples in Real Life
- The apple hanging on a tree.
- A bow pulled back, ready to shoot an arrow.
- A rock sitting on a cliff.
- A basketball held before a throw.
- A child sitting at the top of a slide.
Memory Hack:
If the object is waiting → it’s potential energy.
When to Use Kinetic Energy
Use kinetic energy when:
- The object is moving
- The movement creates energy
- Speed or motion is involved
Examples in Real Life
- A flowing river
- A bike moving down the street
- A child sliding down the slide
- A thrown football
- A spinning fan
Memory Hack:
If it’s moving, it’s kinetic. Movement = Kinetic.
Quick Recap: Potential vs Kinetic Energy
- Potential = stored energy
- Kinetic = moving energy
- Potential becomes kinetic when movement starts
- Kinetic can turn back into potential when movement stops
- Simple rule: Stop = Potential. Move = Kinetic.
Advanced Tips (For Curious Students)
- The word “potential” comes from the Latin word potentia, meaning “power.”
- The word “kinetic” comes from the Greek word kinesis, meaning “movement.”
- In science exams, definitions are usually short:
- Potential: Energy due to position
- Kinetic: Energy due to motion
- In real life, many machines use both energies.
Example: A pendulum swings — potential at the top, kinetic in the middle.
Mini Quiz: Test Yourself!
Fill in the blanks:
- A car moving on the road has __________ energy.
- A stone resting on a cliff has __________ energy.
- A boy running in the park shows __________ energy.
- A balloon full of air has __________ energy stored inside.
- A falling apple changes from potential to __________ energy.
- A parked bicycle has __________ energy.
- A flying airplane has __________ energy.
(Answers: kinetic, potential, kinetic, potential, kinetic, potential, kinetic)
Conclusion
Understanding “Is energy potential or kinetic?” becomes easy once you know the simple rule: not moving = potential, moving = kinetic. These two types of energy are everywhere in daily life — from riding a bike to dropping a ball. The more you practice identifying them, the faster your science skills will grow.
Remember, learning science is fun when you connect it with real life. Keep exploring, keep asking questions, and you’ll become better every day!
FAQs
1. What is the main difference between potential and kinetic energy?
Potential energy is stored energy. Kinetic energy is moving energy.
2. Can an object have both types of energy?
Yes. Many objects switch between potential and kinetic energy.
3. Is height related to potential energy?
Yes. Higher objects have more potential energy.
4. What type of energy does a running person have?
Kinetic energy, because the person is moving.
5. Does a stretched rubber band have potential or kinetic energy?
Potential energy, because it stores energy until released.

Jenn Ashworth offers clear, engaging explanations of language and usage, helping readers grasp meanings, nuances, and differences with accuracy and ease.