Confused about seen or saw? You’re not alone! Many learners mix these up, but this guide will make it super easy. By the end, you’ll know exactly when to use each word — no mistakes, no stress!
Do you ever ask yourself, “Should I say I saw the movie or I have seen the movie?” If yes, you’re in the right place. English learners often confuse seen or saw because both words describe the act of seeing something in the past.
In this guide, we will explain the meanings, differences, and correct usage of seen and saw, plus provide real-life examples. You’ll also learn memory tricks, common mistakes, and even take a mini quiz to test yourself.
By the end, you’ll be able to use these words confidently in conversations, schoolwork, or writing.
What Does Each Word Mean?
Saw
- Part of speech: Verb (past tense of see)
- Meaning: Used to describe an action that happened at a specific time in the past.
- Examples:
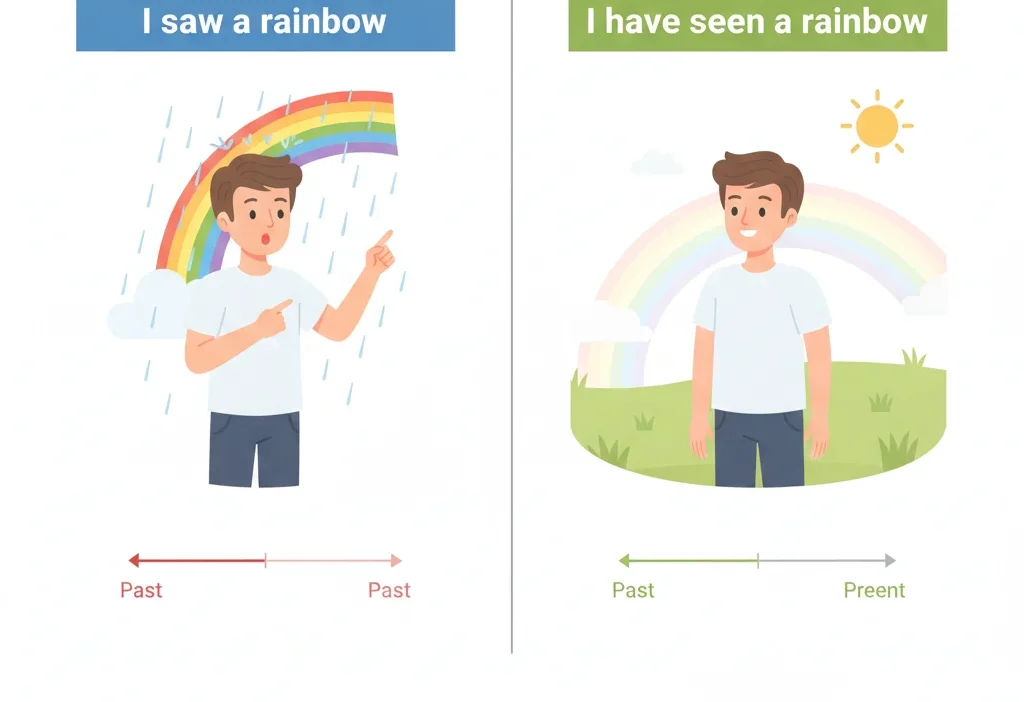
- I saw a rainbow yesterday.
- She saw her friend at the park.
- They saw a shooting star last night.
Tip: Think of saw as the simple past of “see.”
Seen
- Part of speech: Verb (past participle of see)
- Meaning: Used with helping verbs (have, has, had) to describe an experience or something completed.
- Examples:
- I have seen that movie before.
- She has seen my new dress.
- They had never seen such a beautiful sunset.
Tip: You cannot use seen alone; it always needs have/has/had.
The Key Difference Between Seen and Saw
| Word | Meaning | Usage | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Saw | Simple past of see | Use for a past action by itself | I saw a cat in the garden. |
| Seen | Past participle of see | Use with have/has/had | I have seen that cat before. |
Quick Tip: No have/has/had → use saw. With have/has/had → use seen.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
- ❌ I seen the movie yesterday.
✅ Correct: I saw the movie yesterday. - ❌ She saw the movie already.
✅ Correct: She has seen the movie already. - ❌ They seen the rainbow last week.
✅ Correct: They saw the rainbow last week.
Tip: Always check if you need a helping verb. If yes → seen; if no → saw.
When to Use Saw
Use saw for actions that happened at a definite time in the past.
Examples:
- I saw a dog chasing a squirrel this morning.
- We saw a funny movie last night.
- He saw his teacher at the store.
- They saw fireworks on New Year’s Eve.
- She saw a strange bird in the garden.
Tip: Use it for storytelling, daily events, or past activities.
When to Use Seen
Use seen with a helping verb (have, has, had) to talk about experiences or completed actions.
Examples:
- I have seen that movie three times.
- She has seen better days.
- We have seen incredible sunsets on our trips.
- He had seen this problem before.
- They have never seen snow until last winter.
Memory hack: Think of seen as “always needing help” — it cannot stand alone.
Quick Recap: Seen vs Saw
- Saw → simple past, no helping verb: “I saw a cat.”
- Seen → past participle, needs helping verb: “I have seen a cat.”
- Use seen to describe experiences.
- Use saw to describe past events.
- Quick check: Do you need have/has/had? → Use seen. Otherwise → Use saw.
Advanced Tips
- Origin: Both words come from Old English seon, meaning “to see.”
- Formal writing: Always use seen properly with helping verbs.
- Online texting: People often write “I seen it,” which is casual, but in exams or essays, it’s incorrect.
Mini Quiz
Fill in the blanks with saw or seen:
- I ____ a movie last night.
- She has never ____ such a big dog.
- We ____ fireworks on Independence Day.
- He had ____ the same mistake before.
- They ____ a rainbow yesterday.
- Have you ____ this episode already?
- I ____ my favorite singer in concert last year.
Answers:
- saw
- seen
- saw
- seen
- saw
- seen
- saw
FAQs
1. Can I use seen without a helping verb?
No. It always needs have/has/had.
2. Is saw correct in formal writing?
Yes, when describing a past action without a helping verb.
3. What’s a quick trick to remember the difference?
If you need have/has/had, use seen; if not, use saw.
4. Can both words refer to the same event?
Yes, but structure changes: “I saw the movie” (specific event) vs. “I have seen the movie” (experience).
5. Are seen and saw interchangeable?
No. Using them incorrectly changes grammar and clarity.
Conclusion
Now you can confidently use seen or saw. Remember: saw is for past events, and seen is for experiences with a helping verb. Practice these rules daily, notice your mistakes, and soon you’ll be using both words correctly without thinking. Improving your English step by step is easier than you think — and every small improvement counts!

Eley Williams writes clear, engaging guides on confusing words and phrases, helping readers understand meanings, differences, and correct usage with ease.