If you’ve ever paused while writing, wondering whether to use then or than, you’re not alone! These two tiny words look almost the same and sound similar — yet they have completely different meanings. Mixing them up is one of the most common grammar mistakes in English.
In this guide, you’ll learn the difference between “then” and “than,” their meanings, when to use each one, and simple memory tricks to help you never confuse them again. With easy explanations and real-life examples, this article will make understanding then vs than as simple as ABC — perfect for beginners, students, or anyone improving their English grammar skills.
What Does Each Word Mean?
Let’s start by looking at what then and than actually mean.
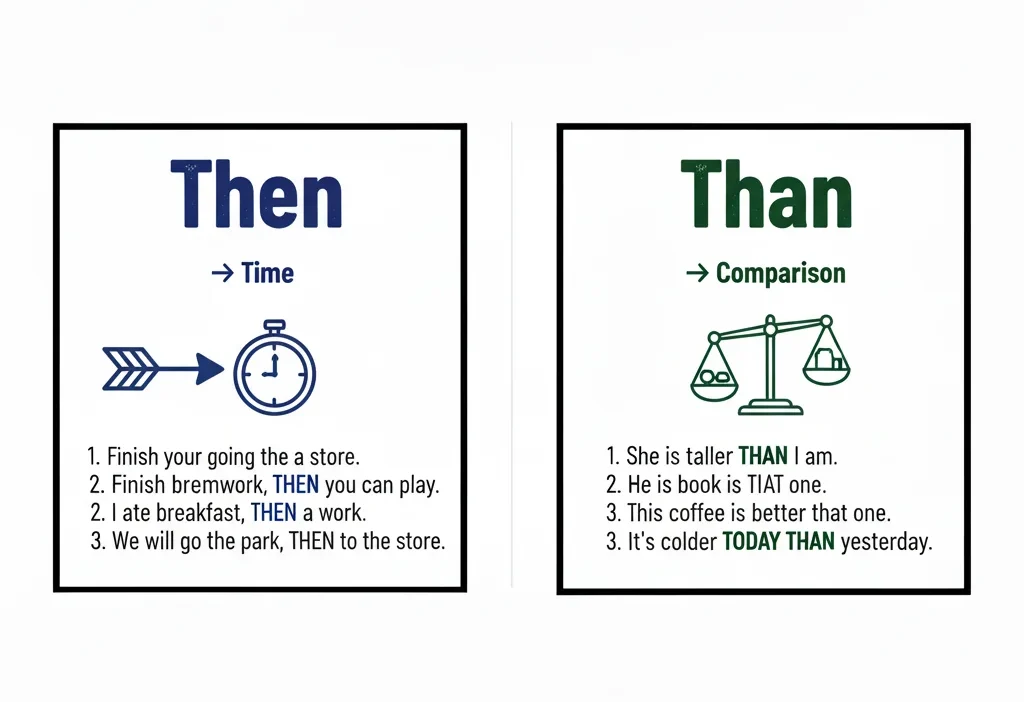
Meaning of “Then”
Then is used to talk about time or order of events. It tells us what happens next, after, or at that time.
It’s an adverb, and sometimes a noun or adjective, depending on the sentence.
Examples of “Then”:
- I finished my homework, then I went to play.
- If you study hard, then you will pass.
- Back then, we didn’t have smartphones.
Think of then as a “timeline word.” It connects moments or steps in time.
Meaning of “Than”
Than is used when comparing two things, people, or ideas.
It’s a conjunction or preposition that shows difference or contrast.
Examples of “Than”:
- My house is bigger than yours.
- She runs faster than her brother.
- I’d rather stay home than go out.
So remember — than = comparison and then = time/order.
A fun story trick:
Imagine “than” as a comparing fan — it loves comparing things.
And “then” as a time-travel friend — it talks about what happens next!
The Key Difference Between Then and Than
Here’s a quick comparison table to make it super clear:
| Word | Meaning | Used For | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Then | Refers to time, sequence, or result | Shows what happens next | I ate dinner, then watched TV. |
| Than | Used for comparison | Shows difference between two things | Ice cream is colder than cake. |
Quick Tip to Remember:
👉 “Then” has an E — like “sEquence” or “timE.”
👉 “Than” has an A — like “compAre.”
210+ Who vs Whom Difference Explained 🗣️ 2025 English Lesson
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Many people mix up these words because they sound similar. Let’s fix that!
❌ Wrong: She is taller then me.
✅ Correct: She is taller than me.
(We’re comparing heights, so we use than.)
❌ Wrong: I finished my exam, than went home.
✅ Correct: I finished my exam, then went home.
(This talks about time — what happened next — so use then.)
Why It Happens:
People often type quickly and swap letters accidentally. But if you slow down and ask yourself,
“Am I talking about time or comparing two things?”
you’ll instantly know which one fits.
When to Use “Then”
Use then when you are:
- Talking about what happens next
- Showing a result or consequence
- Referring to a specific time in the past
Examples:
- We went to the park, then had ice cream.
- If it rains, then we’ll stay inside.
- I was younger then, but I remember clearly.
- Brush your teeth, then go to bed.
- She studied hard; then she passed the test.
Memory Hack:
🕒 Think of “then” as your timeline buddy — it always points to time or order.
When to Use “Than”
Use than when you are:
- Comparing two things or people
- Showing preference or difference
- Expressing choices
Examples:
- My bike is faster than yours.
- He’s more confident than before.
- I’d rather eat fruit than candy.
- This book is better than the movie.
- She is smarter than anyone in her class.
Memory Trick:
⚖️ “Than” is your comparison champion — it always comes between two things being compared.
Quick Recap: Then vs Than
Here’s everything in a nutshell:
- Then → Talks about time or order (What happens next?)
- Than → Used for comparison (What’s different?)
- Then = Time, Than = Comparison
- Example: I’ll eat lunch, then go out.
- Example: I’m hungrier than you.
Quick Rule:
If you can replace the word with next or after that, use then.
If you can replace it with compared to, use than.
Advanced Tips: Going Deeper
1. Origins of Then and Than
Both words come from Old English:
- Then came from “þanne” meaning “at that time.”
- Than came from “þanne” too, but evolved to mean “in comparison with.”
Even back then, people used them differently — just as we do today.
2. In Formal Writing and Exams
In essays, reports, or exams, confusing these words can cost marks.
Always double-check:
- “If… then…” (time or result)
- “More… than…” (comparison)
3. Online & Texting
In casual messages, people often write then instead of than.
Example: “You’re better then me 😅” — this is wrong!
Even in texts, using the right word makes your writing clear and smart.
Mini Quiz: Test Yourself!
Fill in the blanks with then or than:
- I’d rather sleep now _______ watch TV.
- We ate dinner, _______ played games.
- She is taller _______ her brother.
- Back _______, I didn’t have internet.
- This book is more interesting _______ the movie.
- If you finish your homework, _______ you can go out.
- He’s stronger _______ he looks.
(Answers)
- than
- then
- than
- then
- than
- then
- than
FAQs
1. What’s the main difference between “then” and “than”?
“Then” shows time or order; “than” shows comparison.
2. Can I use “then” in place of “than”?
No. They have different meanings and are not interchangeable.
3. How can I remember which to use?
Think then = time, than = comparison.
4. Is “than me” or “than I” correct?
Both can be correct, but “than I” is formal; “than me” is common in speech.
5. Why do people confuse them?
Because they sound alike — but once you remember the “time vs comparison” rule, it’s easy to tell them apart.
Conclusion
You’ve just mastered one of the most confusing grammar pairs in English — then vs than!
Now you know: “then” talks about time or order, while “than” compares two things.
Keep practicing, read carefully, and soon you’ll use both words correctly without even thinking.
Remember — small words make a big difference in clear communication.
Keep learning, keep improving, and enjoy becoming more confident in your English every day! 🌟

Gwendoline Riley delivers clear, compelling insights into language and usage, helping readers understand meanings, nuances, and differences with confidence.